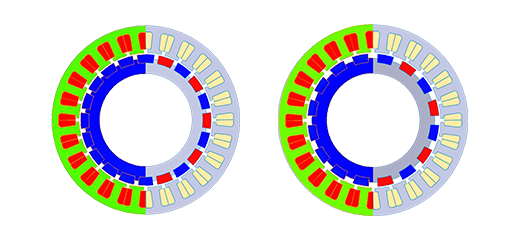
As power electronics and drive systems continue to evolve, specialized electric machines such as Brushless DC (BLDC) motors have emerged as a notable innovation. These motors utilize an electronic controller to regulate DC currents in the stator windings, creating magnetic fields that drive the rotation of a permanent magnet rotor. The transition from traditional brushed motors to BLDC motors is driven by the superior power efficiency, torque effectiveness, compact size, and heightened reliability offered by the latter. BLDC motors have found extensive application in various fields, including robotics, drones, automobiles, and aircraft. Of particular interest are the concentrated windings, enabling more efficient and compact designs by reducing end winding lengths.
This webinar provides a comprehensive, step-by-step demonstration of utilizing EMWorks2D virtual prototyping software for the study and design of two BLDC motor configurations featuring 16 and 20 poles, operating under different commutation conditions (120° and 180° conduction mode). The analysis encompasses vital electromagnetic parameters such as back electromotive force (EMF), flux linkage, average torque, and thermal considerations. Additionally, the session features a demonstration of constructing and simulating a BLDC motor using electromagnetic simulation tools available through EMWorks2D.
As power electronics and drive systems continue to evolve, specialized electric machines such as Brushless DC (BLDC) motors have emerged as a notable innovation. These motors utilize an electronic controller to regulate DC currents in the stator windings, creating magnetic fields that drive the rotation of a permanent magnet rotor. The transition from traditional brushed motors to BLDC motors is driven by the superior power efficiency, torque effectiveness, compact size, and heightened reliability offered by the latter. BLDC motors have found extensive application in various fields, including robotics, drones, automobiles, and aircraft. Of particular interest are the concentrated windings, enabling more efficient and compact designs by reducing end winding lengths.
This webinar provides a comprehensive, step-by-step demonstration of utilizing EMWorks2D virtual prototyping software for the study and design of two BLDC motor configurations featuring 16 and 20 poles, operating under different commutation conditions (120° and 180° conduction mode). The analysis encompasses vital electromagnetic parameters such as back electromotive force (EMF), flux linkage, average torque, and thermal considerations. Additionally, the session features a demonstration of constructing and simulating a BLDC motor using electromagnetic simulation tools available through EMWorks2D.