A direct-drive motor can be directly coupled to the load for high torque and low-speed applications such as washing machines. It helps to eliminate the need for couplings and other mechanical transmissions such as belts and pulleys, gearboxes, etc. The non-direct-drive mechanism has a reduced position accuracy, high mechanical losses, and noise. Whereas the direct-drive mechanism reduces maintenance and improves the system reliability and the overall efficiency as the number of moving parts is reduced.
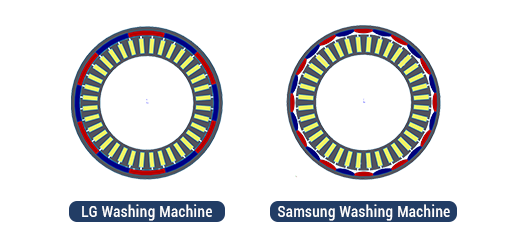
In this webinar, we will demonstrate how to build and simulate two commercial direct-drive outer rotor permanent magnet (PM) motors dedicated for a washing machine application: (i) the bread-loaf surface mounted PM motor topology with 36 slots and 24 poles proposed by the Samsung company and (ii) the surface mounted PM motor having 36 slots and 12 poles commercialized by the LG company. For analysis purposes, the specifications of both motors are kept the same. They only differ by the number of poles and the magnet shapes that lead to a specific winding configuration for each model. In this context, we used our virtual prototyping software tool, EMWorks 2D to design and analyze the performances of the presented motors. The electromagnetic results such as the back EMF, coil flux linkage, and average torque as well as the thermal analysis will be evaluated and analyzed.