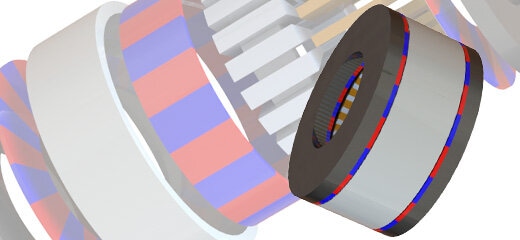
Traditionally, electric motors are either radial-flux or axial-flux; obviously, each configuration has its own pro and cons. To take advantage of both configurations, a hybrid combined radial-axial (RADAX) flux motor configuration has been suggested by several authors. A RADAX motor combines a radial flux motor with one or more axial flux motor, within the same motor housing. RADAX motor has been reported to have several advantages, including enhanced efficiency in low speed, improved volume density and mission capability, a better fault tolerance, and low power operating modes. The RADAX technology is recommended for applications that require high volume density and for vehicles spending a substantial amount of time idling or other low-speed actions. Nevertheless, designing and optimizing a RADAX flux motor is a formidable undertaking that requires not only profound motor design experience but also the best-in-class motor software tools.
To contribute to the understanding of this new and promising technology, we used our virtual prototyping design motor software, EMS, to study and simulate a RADAX flux motor, presented in the journal Energies 20201. In this webinar, we will show you step-by-step how EMS is used to simulate a RADAX flux permanent magnet machine with Halbach-array permanent magnets. We will conclude the webinar by giving you the findings of the author as well as our findings and recommendations.